Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming industries across the globe, and the chemical sector is no exception. From improving safety and efficiency to enabling predictive maintenance and reducing environmental impact, IoT offers immense potential. However, adopting IoT in the chemical industry is not without its hurdles. Understanding these challenges, alongside the opportunities they create, is crucial for companies striving to remain competitive in an increasingly digital world.
Definition
IoT in the chemical industry refers to the integration of Internet of Things technologies – such as sensors, connected devices, and data analytics – into chemical manufacturing and processing. This enables real-time monitoring, improved safety, predictive maintenance, and enhanced efficiency by providing accurate data on equipment performance, environmental conditions, and production processes.
Understanding IoT in the Chemical Industry
The Internet of Things is fundamentally a network of linked gadgets that gather and share data. In the chemical industry, this typically involves sensors, actuators, smart meters, and advanced analytics platforms. These devices can monitor variables such as temperature, pressure, flow rates, chemical composition, and equipment health in real time. By integrating IoT, chemical plants can move from traditional reactive or scheduled maintenance to more dynamic, data-driven operations. This shift helps companies respond more effectively to changing market demands, comply with stringent regulations, and operate more sustainably.
Benefits and Importance of IoT Adoption
Enhanced Operational Efficiency:
IoT enables continuous monitoring and process optimization. By collecting real-time data from production lines, companies can identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks. This results in better use of resources, less downtime, and less energy use.
Improved Safety and Compliance:
Safety is paramount in the chemical industry, given the hazardous nature of many substances involved. IoT solutions such as gas leak detectors and predictive maintenance sensors can help prevent accidents before they occur. Furthermore, IoT facilitates automated compliance reporting, ensuring adherence to environmental and safety regulations.
Predictive Maintenance:
Instead of relying on routine inspections, IoT-driven predictive maintenance uses data analytics to forecast equipment failures. This approach minimizes unplanned outages, extends equipment life, and reduces maintenance costs.
Sustainability and Waste Reduction:
IoT can help monitor emissions, optimize raw material usage, and minimize waste generation. By leveraging this technology, chemical manufacturers can align their operations with sustainability goals and reduce their environmental footprint.
Better Supply Chain Management:
With IoT, chemical companies can track raw materials, in-process goods, and finished products throughout the supply chain. This visibility enhances inventory management, reduces lead times, and improves customer satisfaction.
Challenges Facing IoT Adoption in the Chemical Industry
While the advantages are compelling, adopting IoT in the chemical sector comes with several challenges.
Cybersecurity Risks:
As chemical plants become more connected, they also become more vulnerable to cyberattacks. Hackers targeting industrial control systems could cause catastrophic outcomes, including environmental disasters or operational shutdowns. Ensuring robust cybersecurity for IoT devices and networks is therefore critical.
Legacy Infrastructure Integration:
Many chemical facilities have been operating for decades with legacy systems. These older systems can be difficult and expensive to integrate with contemporary IoT technologies. Retrofitting equipment and ensuring interoperability often requires specialized expertise.
Data Management Complexity:
IoT generates vast amounts of data. Managing this data, ensuring its quality, and extracting actionable insights demand advanced analytics capabilities. Many organizations lack the internal skills or infrastructure to handle big data effectively.
High Initial Costs:
Deploying IoT infrastructure involves significant upfront investment in sensors, connectivity, software platforms, and cybersecurity measures. While the long-term returns can be substantial, the initial financial outlay may deter some companies.
Workforce Adaptation:
Introducing IoT changes the way work is done. Employees may require new skills to interpret data dashboards or manage smart systems. Resistance to change or lack of training can slow down adoption.
Opportunities on the Horizon
Despite these challenges, the opportunities for chemical companies willing to embrace IoT are enormous.
Advanced Process Automation:
IoT lays the foundation for more sophisticated process automation. With real-time data, AI and machine learning algorithms can dynamically adjust chemical processes to maintain optimal conditions, improving yield and reducing variability.
Digital Twins:
A digital twin is an electronic duplicate of a real-world process or item. By feeding IoT data into these models, companies can simulate scenarios, predict outcomes, and test process adjustments without disrupting actual operations. Innovation and risk management are improved by this skill.
Circular Economy Initiatives:
IoT can help chemical companies track materials through their lifecycle, enabling more effective recycling and waste reduction. This supports circular economy models, where resources are reused, contributing to long-term sustainability.
Customer-Centric Production:
With better demand forecasting enabled by IoT data, manufacturers can shift towards more flexible, on-demand production. This reduces inventory costs and enhances responsiveness to customer needs.
Enhanced Collaboration Across the Value Chain:
Sharing IoT-generated data with suppliers and customers fosters greater transparency and collaboration. For instance, chemical producers can provide customers with detailed insights into product quality or delivery timelines.
Navigating the Path Forward
For chemical companies looking to harness IoT, a strategic approach is essential. Here are a few key steps:
- Start small and scale: Pilot projects focused on specific challenges, such as energy management or predictive maintenance, allow companies to build expertise and demonstrate ROI before scaling up.
- Invest in cybersecurity: A comprehensive security strategy, including secure device configurations, encrypted communications, and regular audits, is critical to protect sensitive operations.
- Develop data governance policies: Clear protocols for data collection, storage, analysis, and sharing help maximize the value of IoT while complying with regulatory requirements.
- Upskill the workforce: Training employees to work with digital tools and fostering a culture of innovation are fundamental to successful IoT integration.
- Collaborate with technology partners: Partnerships with IoT platform providers, cybersecurity firms, and system integrators can accelerate deployment and reduce implementation risks.
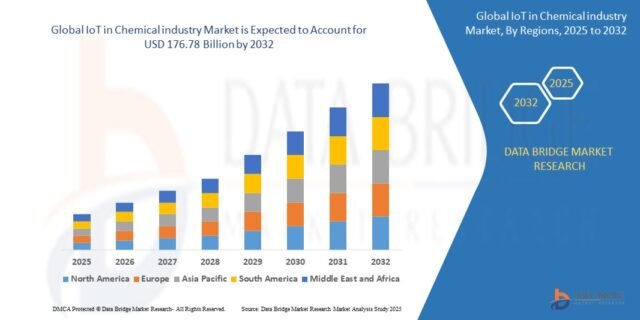
Growth Rate of IoT in Chemical industry Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the IoT in chemical industry market was estimated to be worth USD 78.79 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.63% to reach USD 176.78 billion by 2032.
For more insights on the autoimmune disease treatment Market visit:
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-iot-in-chemical-industry-market
Conclusion
The chemical industry stands to benefit from safer, more effective, and more sustainable operations through the implementation of IoT. While challenges such as cybersecurity risks, integration complexities, and skills gaps must be carefully managed, the opportunities far outweigh the obstacles. By embracing IoT thoughtfully, chemical companies can position themselves at the forefront of digital transformation, driving competitiveness and long-term growth in an increasingly connected world.






